Flexible Packaging
Everything You Need to Know About Flexible Packaging
Flexible packaging is packaging material that conforms to fit the shape of its contents as opposed to maintaining a consistent form. Available in a variety of designs, materials, and finishes, this type of packaging finds application holding and protecting a wide range of liquid and solid products. Compared to rigid packaging, it offers a number of advantages, such as lower material requirements and manufacturing costs. These advantages can result in a significant increase in the profitability of a business.
Thinking of choosing flexible packaging for your products? Here’s everything you need to know to make an informed decision as to whether it’s right for your product needs.



![]()

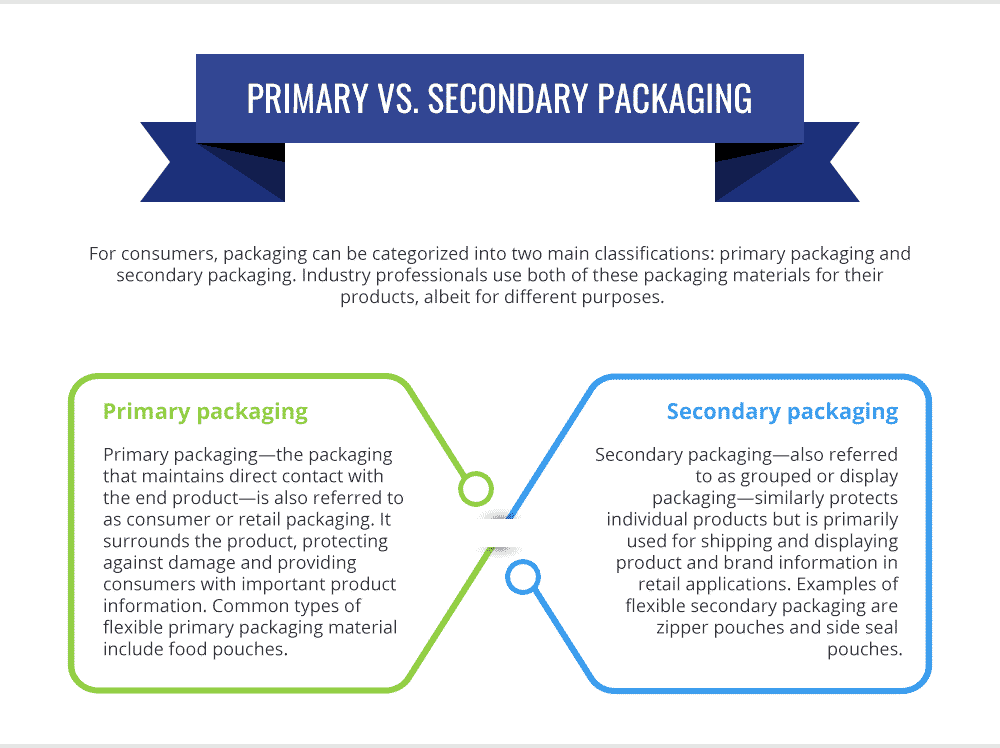
Primary vs. Secondary Packaging
For consumers, packaging can be categorized into two main classifications: primary packaging and secondary packaging. Industry professionals use both of these packaging materials for their products, albeit for different purposes.
- Primary packaging—the packaging that maintains direct contact with the end product—is also referred to as consumer or retail packaging. It surrounds the product, protecting against damage and providing consumers with important product information. Common types of flexible primary packaging material include food pouches.
- Secondary packaging—also referred to as grouped or display packaging—similarly protects individual products but is primarily used for shipping and displaying product and brand information in retail applications. Examples of flexible secondary packaging are zipper pouches and side seal pouches.
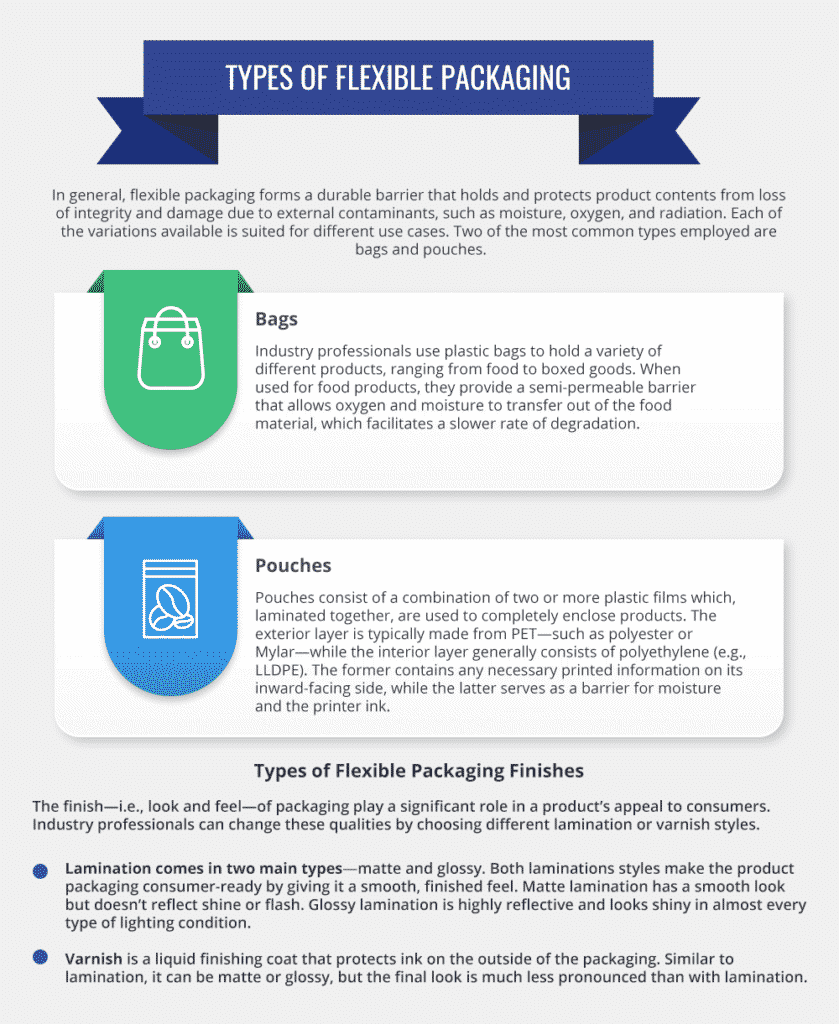
Types of Flexible Packaging
In general, flexible packaging forms a durable barrier that holds and protects product contents from loss of integrity and damage due to external contaminants, such as moisture, oxygen, and radiation. Each of the variations available is suited for different use cases. Two of the most common types employed are bags and pouches.
Bags
Industry professionals use plastic bags to hold a variety of different products, ranging from food to boxed goods. When used for food products, they provide a semi-permeable barrier that allows oxygen and moisture to transfer out of the food material, which facilitates a slower rate of degradation.
PouchesPouches consist of a combination of two or more plastic films which, laminated together, are used to completely enclose products. The exterior layer is typically made from PET—such as polyester or Mylar—while the interior layer generally consists of polyethylene (e.g., LLDPE). The former contains any necessary printed information on its inward-facing side, while the latter serves as a barrier for moisture and the printer ink.
Types of Flexible Packaging FinishesThe finish—i.e., look and feel—of packaging play a significant role in a product’s appeal to consumers. Industry professionals can change these qualities by choosing different lamination or varnish styles.
- Lamination comes in two main types—matte and glossy. Both laminations styles make the product packaging consumer-ready by giving it a smooth, finished feel. Matte lamination has a smooth look but doesn’t reflect shine or flash. Glossy lamination is highly reflective and looks shiny in almost every type of lighting condition.
- Varnish is a liquid finishing coat that protects ink on the outside of the packaging. Similar to lamination, it can be matte or glossy, but the final look is much less pronounced than with lamination.
5 Advantages of Flexible Packaging vs. Rigid Packaging
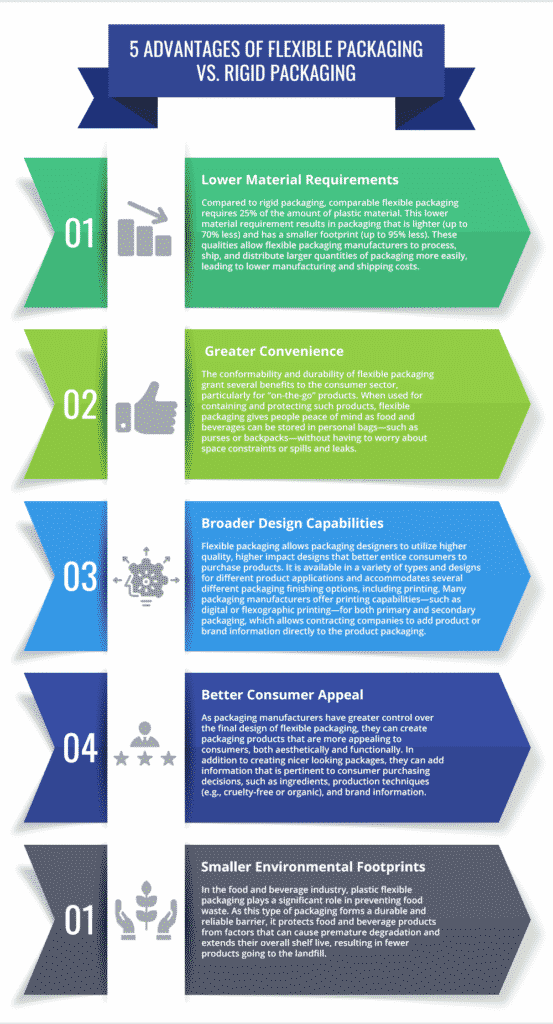
Flexible packaging offers several advantages over its rigid counterpart, such as:
1. Lower Material Requirements
Compared to rigid packaging, comparable flexible packaging requires 25% of the amount of plastic material. This lower material requirement results in packaging that is lighter (up to 70% less) and has a smaller footprint (up to 95% less). These qualities allow flexible packaging manufacturers to process, ship, and distribute larger quantities of packaging more easily, leading to lower manufacturing and shipping costs.
2. Greater Convenience
The conformability and durability of flexible packaging grant several benefits to the consumer sector, particularly for “on-the-go” products. When used for containing and protecting such products, flexible packaging gives people peace of mind as food and beverages can be stored in personal bags—such as purses or backpacks—without having to worry about space constraints or spills and leaks.
3. Broader Design Capabilities
Flexible packaging allows packaging designers to utilize higher quality, higher impact designs that better entice consumers to purchase products. It is available in a variety of types and designs for different product applications and accommodates several different packaging finishing options, including printing. Many packaging manufacturers offer printing capabilities—such as digital or flexographic printing—for both primary and secondary packaging, which allows contracting companies to add product or brand information directly to the product packaging.
4. Better Consumer Appeal
As packaging manufacturers have greater control over the final design of flexible packaging, they can create packaging products that are more appealing to consumers, both aesthetically and functionally. In addition to creating nicer looking packages, they can add information that is pertinent to consumer purchasing decisions, such as ingredients, production techniques (e.g., cruelty-free or organic), and brand information.
5. Smaller Environmental Footprints
In the food and beverage industry, plastic flexible packaging plays a significant role in preventing food waste. As this type of packaging forms a durable and reliable barrier, it protects food and beverage products from factors that can cause premature degradation and extends their overall shelf live, resulting in fewer products going to the landfill.